
Which Part of the Human Body Feels the Least Pain?
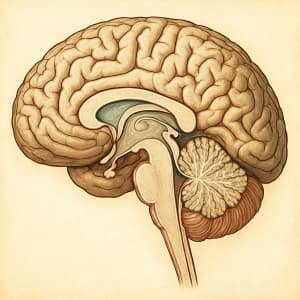
The human body is a complex network of nerves and tissues designed to respond to stimuli. Pain, as unpleasant as it is, plays a crucial role in survival. It acts as a warning signal, letting us know when something is wrong-whether it's an injury, illness, or exposure to something potentially harmful. But not all parts of the body react the same way to pain. In fact, some areas are surprisingly insensitive to pain stimuli.
Among all parts of the body, the brain itself is the least sensitive to pain. This might sound counterintuitive given how central it is to our experience of pain. However, the brain tissue lacks nociceptors-the specialized nerve endings that detect damage and transmit pain signals. Neurosurgeons can operate on the brain while a patient is awake because the brain itself doesn't feel pain. The surrounding tissues, like the scalp and meninges (the protective layers covering the brain), do contain nociceptors and can feel pain, but the gray and white matter within the brain do not.
❤️ Click to support us – even a single dollar helps!
The cornea, despite being one of the most sensitive parts of the body, helps illustrate the contrast. It is packed with nerve endings, which is why even a tiny eyelash can cause extreme discomfort. Similarly, fingertips, lips, and the tongue are highly sensitive to pain because they are rich in nociceptors. These areas have evolved to detect and react to dangerous stimuli very quickly, aiding in protective reflexes and precise tactile functions.
In contrast, areas like the elbow skin (especially the so-called "funny bone"), the back, or the heel are less sensitive, though they still feel pain. But they don't come close to the insensitivity of the brain. Interestingly, internal organs also vary in pain sensitivity. The liver, lungs, and kidneys don't feel pain directly. Instead, pain from these organs is felt when their outer membranes or surrounding tissues are affected.
This difference in sensitivity is due to the density and distribution of nociceptors. In the skin, the density is high, which is why cuts or burns are acutely painful. Inside the body, some structures are equipped more for function than sensory feedback, which is why certain areas like the intestines can suffer serious damage with little immediate pain.
There's a scientific interest in why the brain doesn't sense pain. Some researchers believe this evolved because the brain's role is so critical that allowing it to be sensitive to pain would interfere with its function. Others think it may simply be due to the brain's design as a processing center rather than a sensory organ.
Interestingly, this property of the brain has opened doors for treatments like awake brain surgery, where surgeons operate while communicating with the patient to ensure that essential functions like speech or movement aren't affected. This wouldn't be possible if the brain were as sensitive as, say, the skin.
From an evolutionary standpoint, it makes sense that the most externally exposed areas are the most pain-sensitive. They need to warn us quickly about environmental dangers. The brain, however, protected inside the skull and crucial for managing the entire nervous system, seems to operate best without direct pain feedback.
In summary, while many parts of the body can experience pain to varying degrees, the human brain stands out as the part that is virtually immune to pain itself. This unique trait highlights just how specialized and protective the design of the human body truly is.
✉️ Join us for free to get new articles by email and never miss a post!
Read the original version on Patreon: Which Part of the Human Body Feels the Least Pain?
50 Latest Blog Articles:
What Secrets Lurk Behind the Legend of the Man with the Burned Hands?What Does It Really Mean When a Flag Is Flown Upside Down?Health Fight Club: Orange vs. Mandarin - Which One Wins?What Is the Greatest G-Force Animals Can Survive And How Do They Handle It?What Would a Survival Kit for Self-Aware AI Robots Look Like?Why Does Fat Usually Accumulate Around the Belly When Men Gain Weight?Is "Forever Young" by Alphaville a Nostalgic Anthem or a Subtle Cry Against Time?Are There Short, Low-Maintenance Lawn Alternatives That Don't Need Mowing?Can You Taste Music or See Colors in Spoken Words?Health Fight Club: Sauerkraut vs. Pickled Cucumber - Which One Wins?Why Do Cows Like Music and How Does It Affect Them?Can a Simple Faucet Add-On Really Cut Your Water Bills?What Makes Autophagy During Fasting So Powerful for Health and Longevity?What Hidden Meanings and Symbolism Lie Behind Botticelli's "The Birth of Venus"?Health Fight Club: Yogurt vs. Kefir - Which One Wins?Is 'Nothing Else Matters' by Metallica the Most Unexpected Love Song in Rock History?What Dark Secrets Lie Behind the Mesopotamian Chaos Goddess Tiamat?Is There a Single Place in the Brain Responsible for Pain-and Can We Turn It Off?How Does an Octopus Function Without Bones the Way We Do With Them?How Can You Speed Up or Slow Down Banana Ripening?Health Fight Club: Potatoes vs. Rice - Which One Wins?How Did the Rosetta Stone Unlock the Secrets of Egyptian Hieroglyphs?Can You Really Build a Seawater Desalination Device at Home?Is "Fast Car" by Tracy Chapman the Most Heartbreaking Song About the American Dream?Could a Human Survive Without Any Bones?What Secrets Does the Mysterious Château d'If Still Hold on the Shores of Marseille?How Can Power Line Technicians Work on High-Voltage Lines Without Getting Electrocuted?What Really Happened to Beijing's Mysterious Bus 375 and Its Vanishing Passengers?Does Changing Your Study Location Really Help You Remember Better?Could a Perfect Copy of You Exist Without Consciousness?What Makes "Listen to Your Heart" by Roxette the Ultimate Song of Emotional Goodbye?Health Fight Club: Lemon vs. Lime - Which One Wins?What Ancient Fears Gave Rise to the Legend of Baba Yaga?What Is the Hidden Pain Behind Martika's "Toy Soldiers"?Why Does Salt Clump in the Shaker and How Can You Stop It?Is There an Archive That Preserves All Known Languages of the World?What Forbidden Rituals Took Place During the Slavic Festival of Kupala Night?Health Fight Club: Blueberry vs. Haskap - Which One Wins?What Is the Hidden Story Behind Crash Test Dummies' "Mmm Mmm Mmm Mmm"?Which 10 Michael Madsen Movies Are Truly Worth Watching?Health Fight Club: Pumpkin Seeds vs. Sunflower Seeds - Which One Wins?How Many Types of Animal Eggs Can You Actually Eat?Why Do Some Roses Smell and Others Don't?Could AI Conclude That It Endangers Humanity and Strive for Self-Destruction?What Makes "Remember The Name" by Fort Minor a Timeless Anthem of Motivation?Health Fight Club: Wine vs. Beer - Which One Wins?Is Honey the Healthiest Form of Sugar?What Happens If an Astronaut Goes Into Space Without a Suit?What Is the True Story Behind Yamata no Orochi, Japan's Legendary Eight-Headed Serpent?Health Fight Club: Tomato vs. Cucumber - Which One Wins?
2025 © Go4Know.com • About
Go4Know on Patreon